Using Environment Variables with IaC Projects
Flightcontrol supports setting environment variables for your projects configured with the flightcontrol.json file.
Because we’ve found that our users need a lot of flexibility when it comes to setting environment variables, we supply several different ways to configure them.
- In the dashboard
- In the
flightcontrol.jsonfile
Read on to learn more about each of these methods.
Setting Environment Variables in the Dashboard
Although you may be using flightcontrol.json to configure your project, you can still set environment variables in the dashboard. These values will be merged with the values in flightcontrol.json, but will not override any values set in the configuration file.
Setting Environment Variables in flightcontrol.json
Within your flightcontrol.json file, you can set environment variables with the envVariables property. This property is an object, which can be placed at one of three levels:
- The top level (for the entire project)
- For an individual environment
- For an individual service within an environment.
Example Environment Variables Configuration
In the following example, we set two environment variables on the web-server service - one for the app environment, and one as the database connection URL, pulled in from the db service.
"services": [
{
"id": "web-server",
"name": "Web Server",
"type": "web",
"target": {
"type": "fargate"
},
"buildType": "nixpacks",
"ci": {
"type": "ec2"
},
"cpu": 0.5,
"memory": 1,
"minInstances": 1,
"maxInstances": 1,
"envVariables": {
"APP_ENV": "production",
"DATABASE_URL": {
"fromService": {
"id": "db",
"value": "dbConnectionString"
}
}
}
},
{
"id": "db",
"name": "Database",
"type": "rds",
"engine": "postgres",
"engineVersion": "15",
"instanceSize": "db.t4g.micro",
"storage": 20,
"private": false
}
]Runtime-only Environment Variables in flightcontrol.json
For each service in your flightcontrol.json file, you can set the includeEnvVariablesInBuild property to true or false. This property is true by default. To enable runtime-only behavior, set this property to false.
{
"services": [
{
"id": "webapp",
"name": "Web App",
"type": "web",
"target": {"type": "fargate"},
"buildType": "nixpacks",
"ci": {
"type": "ec2"
},
"cpu": 0.5,
"memory": 1,
"minInstances": 1,
"maxInstances": 2,
"envVariables": {
"SECRET_API_KEY": "ABC-123"
},
"includeEnvVariablesInBuild": false
}
]
}Different Types of Environment Variables
Due to the number of different ways you can set environment variables, we’ve broken them down into different types.
Static Environment Variables
These are hard coded values in the flightcontrol.json file.
- Format:
"NAME": "<value>" - Example:
"APP_ENV": "production"Environment Variables from another service
These are very useful when making connections between services - for instance, when you need to connect to a database from your web server. Or if you need to connect to your API Server from your static Single Page Application build.
- Format:
"NAME": {"fromService": {"id": "<serviceId>", value: "<value>"}} - Example:
"USER_DATABASE_URL": {
"fromService": {
"id": "db",
"value": "dbConnectionString"
}
}The following sections contain the specific environment variables you can pull from each service type.
From Database Services
dbConnectionStringwill be the connection URL for the database instance:postgres://username:password@host:port/dbNameusername, password, host, portwill be the individual connection information for the database instance
Additionally, for Database Preview Environments
dbNamewill be the name of the databasedbEnginewill be the database engine (postgres, mysql, etc)
From Redis Services
connectionStringwill be the connection URL for the Redis instance:rediss://www.example.com:6379authToken, host, portwill be the individual connection information for the primary ElastiCache nodereaderConnectionString, readerHost, readerPortwill contain the connection information to split connections evenly between the read replica nodes in the ElastiCache cluster (with cluster mode disabled)
From Web and Private Web Services
hostwill include the CloudFront service URL without protocol. Example:www.example.comoriginwill include the CloudFront service URL with protocol. Example:https://www.example.comloadBalancerHostwill include the application load balancer service URL without protocol. Example:app.fctl.apploadBalancerOriginwill include the application load balancer service URL with protocol. Example:https://app.fctl.app
From Network and Private Network Server Services
loadBalancerHostwill include the network server service URL without protocol. Example:app.fctl.apploadBalancerPort${portNumber}will include the port number for the application load balancer. Example:loadBalancerPort80
From Static Services
hostwill include the CloudFront service URL without protocol. Example:www.example.comoriginwill include the CloudFront service URL with protocol. Example:https://www.example.com
From S3 buckets
bucketNamewill be the S3 bucket name
From Lambda Function Services
hostwill include the Lambda function URL without protocol. Example:example.lambda-url.region.on.awsoriginwill include the Lambda function URL with protocol. Example:https://example.lambda-url.region.on.awslambdaArnwill include the ARN of the Lambda functionlambdaAliasArnwill include the ARN of the Lambda alias
Environment Variables from Parameter Store
Securely retrieve the value from AWS Parameter Store. Parameter Store is a free AWS service for securely storing secrets.
Important: Your parameter store item must be in the same AWS region as your service
- Format:
"NAME": {"fromParameterStore": "<parameterStoreItemName>"} - Example:
"STRIPE_API_KEY": {
"fromParameterStore": "ACME_STRIPE_API_KEY"
}Creating a Parameter on the AWS Parameter Store: 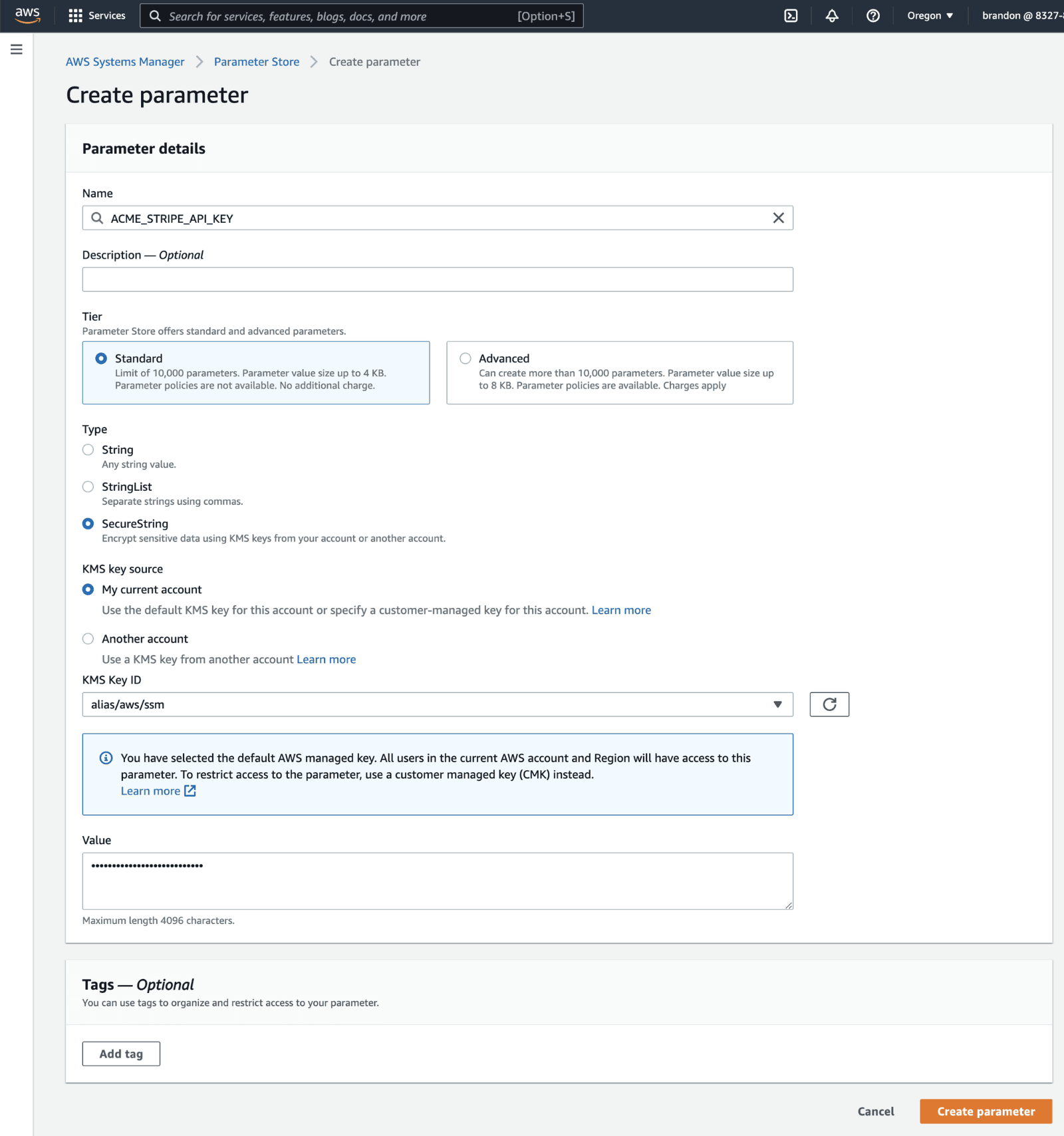
Environment Variables from Secrets Manager
Securely retrieve the value from AWS Secrets Manager. Secrets Manager is a paid AWS service for securely storing secrets. It costs $0.40/secret/month
- Format:
"NAME": {"fromSecretsManager": "<arn:your-secret-arn>"} - Example:
"STRIPE_API_KEY": {
"fromSecretsManager": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-west-1:832786265645:secret:/stripe-y6uINZ"
}Environment Variables set by Flightcontrol
Flightcontrol sets several environment variables for your project, which you can use during builds or runtime for your application.
For a complete list of the environment variables set by Flightcontrol that your project can use, see the Built-in Environment Variables section of the Environment Variables docs.